Penis Cancer Symptoms: Penile cancer lump symptoms
When malignant cells in your penis proliferate out of control, penile cancer results. Although it is uncommon in the United States, you should visit your doctor if you observe any changes to your penis, such as a lump or discoloration. Early intervention can stop the cancer from spreading. Treatment for penile cancer that has metastasized to other body areas is more difficult.
Definition of Penis Cancer
Penis cancer is a type of malignancy that occurs in the tissues of the penis. Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Comprehensive Guide to Penile Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Penile cancer is a rare but serious condition characterized by malignant growths in the penis. Understanding the signs, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management. This detailed guide will cover the essentials of penile cancer, including symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
What is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer occurs when malignant cells in the penis grow uncontrollably. While it is relatively uncommon in the United States, it is more prevalent in other regions, including parts of Africa, Asia, and South America. Penile cancer primarily affects older men, but it can occur in younger individuals as well. The disease typically starts in the skin of the penis, particularly on the glans (head) or the foreskin in uncircumcised men. Read More articles: Can A Prolapse Be A Sign Of Cancer
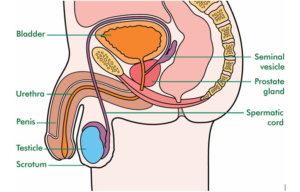
Understanding the Penis: Anatomy and Function
The penis serves two primary functions: expelling urine and delivering sperm during sexual intercourse. It comprises three main tubes:
- Urethra: A hollow tube that carries urine from the bladder and semen out of the body.
- Corpora Cavernosa: Two spongy tubes that fill with blood to produce an erection.
- Tunica Albuginea: A tough fibrous sheath surrounding the corpora cavernosa.
During an erection, the corpora cavernosa fill with blood, causing the penis to become rigid, allowing for sexual intercourse.
Penile Cancer Signs and Symptoms
Early detection of penile cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes. Recognizing penile cancer signs is crucial. Common symptoms of penile carcinoma include:
- A painless lump or sore that may bleed.
- Skin thickening or changes in color.
- A reddish, velvety rash.
- Small, crusty bumps or flat, bluish-brown growths.
- Swelling or unusual swelling in the penis.
- Smelly discharge under the foreskin.
- Non-healing sores or ulcers that may bleed.
- Penile cancer bleeding symptoms or discharge symptoms.
- Penile cancer irritation symptoms or painful symptoms.
Penile cancer indicators often include changes in skin and sensitivity symptoms. Symptoms may start as minor irritations, which can escalate to more severe issues if not addressed promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing penile cancer:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This sexually transmitted virus is linked to many penile cancer cases. HPV-16, in particular, is associated with higher risk.
- Phimosis: A condition where the foreskin cannot be retracted, potentially increasing the risk of cancer.
- Poor Hygiene: Accumulation of smegma under the foreskin can lead to irritation and inflammation.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using other tobacco products is a known risk factor.
- HIV Infection: HIV-positive individuals may have a higher risk due to associated behaviors and immune system impact.
- Lichen Sclerosus: An inflammatory condition that can increase cancer risk.
- PUVA Treatment: Used for psoriasis, this treatment involves ultraviolet radiation, which can raise cancer risk.
Understanding these penile cancer risk factors helps in preventive measures and early intervention.
Diagnosis of Penile Cancer
Accurate diagnosis of penile cancer involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: The healthcare provider examines the penis for unusual penile symptoms, such as lumps or discoloration.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed and analyzed under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells. This helps in identifying the penile cancer lump symptoms and staging the cancer.
- Imaging Tests: If cancer is suspected to have spread, imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be used to determine the extent of metastasis.
Penile cancer is staged using the TNM staging system, which assesses:
- T (Tumor): The size and extent of the primary tumor.
- N (Nodes): Spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M (Metastasis): Spread to other organs.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment depends on the stage and extent of the cancer:
- Topical Medications: For early-stage cancer, medicated creams like fluorouracil or imiquimod can be effective.
- Surgery: Options include local excision, Mohs surgery (removing cancer layer by layer), and more extensive surgeries for advanced cancer. Penectomy may be necessary for severe cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Used to target cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: May be used to treat advanced cancer or in combination with other therapies.
Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor for recurrence and manage any post-treatment symptoms.
Preventing Penile Cancer

While there is no guaranteed way to prevent penile cancer, several measures can reduce the risk:
- Circumcision: Circumcising infants reduces cancer risk later in life. For those not circumcised, maintaining good genital hygiene is crucial.
- HPV Vaccination: Vaccines like Gardasil and Cervarix can help protect against high-risk HPV strains.
- Safe Sex Practices: Using condoms and reducing the number of sexual partners can lower HPV risk.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Reducing or eliminating tobacco use can decrease cancer risk.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Early detection through self-examination and regular visits to the healthcare provider can catch issues before they become severe.
Living with Penile Cancer
The impact of penile cancer on daily life varies. Many treatments preserve penile function, allowing individuals to maintain normal urination and sexual activities. However, more extensive surgeries may alter these functions.
Penile cancer and treatment can lead to various symptoms, including changes in how you urinate or experience sexual activity. Open communication with healthcare providers about any concerns or changes is essential for managing these effects.
Key Takeaways
- Early Detection: Regular self-examination and awareness of penile cancer signs are vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Risk Factors: Understanding and managing penile cancer risk factors can help in prevention.
- Treatment and Management: Effective treatment options are available, but timely intervention is crucial.
- Prevention: Good hygiene, HPV vaccination, and avoiding tobacco can reduce risk.
Regular check-ups and prompt action on unusual penile symptoms are the best strategies for managing and preventing penile cancer. If you notice any changes in your penis, seek medical advice immediately to ensure timely and effective treatment.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for tackling penis cancer effectively.
Encouragement for Regular Health Checks
Regular health checks empower individuals to take control of their well-being, promoting early detection and better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Can penis cancer be prevented?
A. While not entirely preventable, practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated against HPV, and maintaining good personal hygiene can reduce the risk.
Q. Are there support groups for individuals with penis cancer?
A. Yes, various support groups provide emotional support and a sense of community for those affected by penis cancer.
Q. Is surgery the only treatment option for penis cancer?
A. No, treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy, depending on the individual case.
Q. What age group is most at risk for penis cancer?
A. Penis cancer risk increases with age, with older individuals being more susceptible.
Q. How often should one undergo medical check-ups for early detection?
A. Regular check-ups, at least annually, are recommended for early detection of potential health issues, including penis cancer.