Is Emphysema Cancer
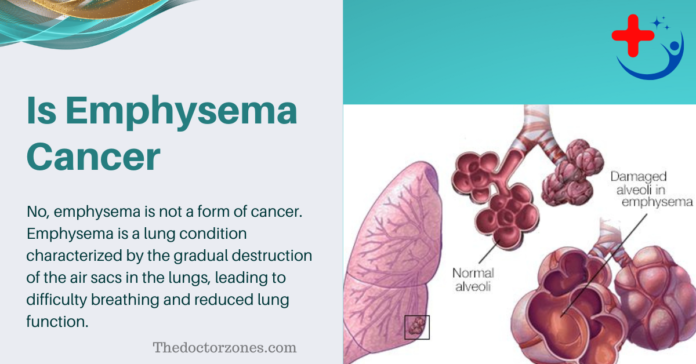
No, emphysema is not a form of cancer. Emphysema is a lung condition characterized by the gradual destruction of the air sacs in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing and reduced lung function. It is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke or pollutants. Read more Is Heel Pain a Sign of Cancer
Cancer, on the other hand, refers to the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. It can occur in various organs, including the lungs. Lung cancer is a distinct condition from emphysema, although both can be caused by smoking and share some symptoms, such as shortness of breath. It’s important to differentiate between these two conditions as their causes, treatments, and outcomes are different.
Understanding Emphysema
What is Emphysema?
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that falls under the umbrella of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is characterized by the gradual destruction of the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, leading to reduced lung function and airflow obstruction. Emphysema is commonly caused by long-term exposure to harmful substances like cigarette smoke or environmental pollutants.
Emphysema Symptoms
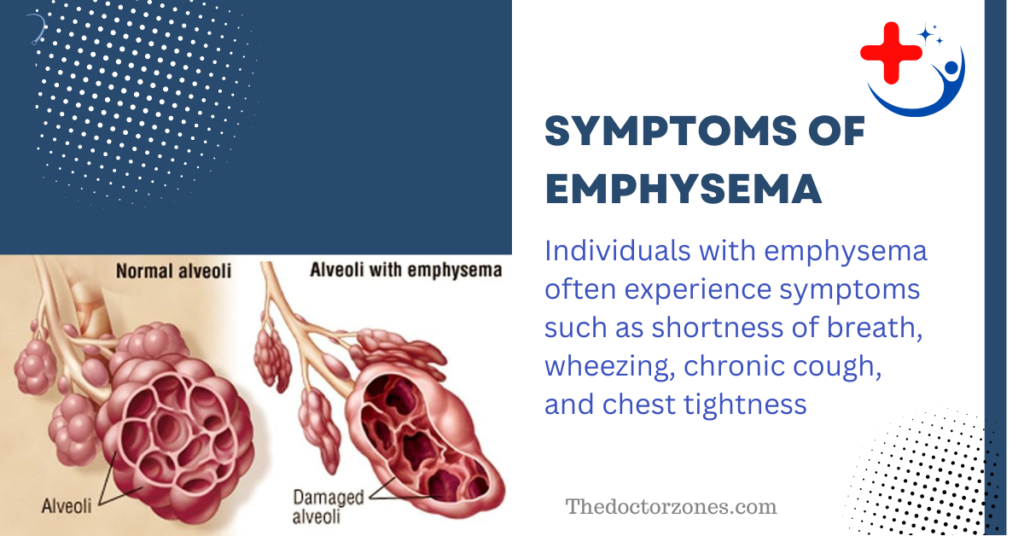
Individuals with emphysema often experience a range of symptoms that can progressively worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chronic cough
- Chest tightness
- Increased mucus production
- Fatigue and tiredness
Emphysema Causes
The primary cause of emphysema is long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways. These include:
- Smoking: The leading cause of emphysema, accounting for the majority of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke from others’ cigarettes.
- Air Pollution: Environmental pollutants can contribute to lung damage.
- Occupational Hazards: Inhalation of dust, chemicals, and fumes in the workplace.
- Genetics: Certain genetic factors, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, can increase the risk of developing emphysema.
How Does Emphysema Affect the Lungs?
In emphysema, the walls of the alveoli are gradually destroyed, leading to the formation of larger but fewer air sacs. This reduces the surface area available for gas exchange, making it difficult for the lungs to transfer oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide. As the disease progresses, breathing becomes increasingly labored, and the lungs lose their elasticity, trapping air and making it harder to expel. Also read the Article: What Percentage of Positive Cologuard Tests Are Cancer
Emphysema Diagnosis
Diagnosing emphysema typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests, including:
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Measure lung function and airflow.
- Chest X-ray: Provides images of the lungs to detect changes associated with emphysema.
- CT Scan: Offers detailed images of the lungs and airways.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
Emphysema Treatment
While there is no cure for emphysema, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics to manage symptoms and prevent infections.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen to help maintain adequate oxygen levels.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Exercise and education programs to improve lung function and overall health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, avoiding pollutants, and adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Surgery: In severe cases, procedures such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant may be considered.
Emphysema Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with emphysema varies depending on the severity of the disease, overall health, and lifestyle choices. While the disease is progressive and chronic, early diagnosis and proper management can help slow its progression and improve quality of life. Discover what Can Mold Cause Cancer
Can Emphysema Be Prevented?
Preventing emphysema primarily involves reducing exposure to known risk factors. Key preventive measures include:
- Quitting Smoking: The most effective way to prevent emphysema.
- Avoiding Secondhand Smoke: Limiting exposure to smoke from others.
- Protecting Against Occupational Hazards: Using protective equipment and following safety guidelines in the workplace.
- Minimizing Exposure to Air Pollution: Staying indoors on high pollution days and using air purifiers.
Exploring Lung Cancer
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the lungs. These cells can invade and destroy surrounding tissues and potentially spread to other parts of the body (metastasis). Lung cancer is broadly categorized into two main types:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, accounting for about 85% of cases.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): A more aggressive form that spreads quickly.
Lung Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of lung cancer can vary widely depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Back pain
- Tumor formation
Lung Cancer Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing lung cancer, including:
- Smoking: The leading cause of lung cancer, responsible for about 90% of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Inhalation of smoke from others can also increase risk.
- Radon Exposure: A radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and increase cancer risk.
- Asbestos Exposure: Occupational exposure to asbestos fibers.
- Family History: Genetics can play a role in lung cancer risk.
- Environmental Pollutants: Air pollution and exposure to certain chemicals.
How is Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing lung cancer involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests, such as:
- Imaging Tests: Chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI, and PET scan to detect and evaluate tumors.
- Biopsy: Removal of a tissue sample for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Sputum Cytology: Examination of mucus coughed up from the lungs.
- Molecular Testing: Identifying specific genetic mutations in cancer cells to guide treatment.
Lung Cancer Treatment
Treatment options for lung cancer depend on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue, often used in early-stage cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill or stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
- Palliative Care: Managing symptoms and improving quality of life for advanced cancer.
Emphysema vs. Lung Cancer
Difference Between Emphysema and Lung Cancer
While emphysema and lung cancer are both serious lung diseases, they are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Here are the key differences:
- Nature of the Disease: Emphysema is a chronic lung disease characterized by the destruction of alveoli, while lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lungs.
- Causes: Emphysema is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, while lung cancer is most commonly linked to smoking but can also result from genetic factors, radon exposure, and other environmental pollutants.
- Symptoms: While both diseases share symptoms like shortness of breath and chronic cough, lung cancer often presents additional symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, coughing up blood, and tumor formation.
- Diagnosis: Emphysema is diagnosed through pulmonary function tests, imaging, and blood gas analysis, while lung cancer diagnosis involves imaging tests, biopsies, and molecular testing.
- Treatment: Emphysema treatment focuses on symptom management and improving lung function through medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes. Lung cancer treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Connection Between Emphysema and Lung Cancer
While emphysema itself is not cancer, there is a notable connection between the two conditions. Individuals with emphysema may have a higher risk of developing certain types of lung cancer. This increased risk is largely attributed to shared risk factors, primarily smoking. The damage caused by smoking can lead to both emphysema and lung cancer, emphasizing the importance of smoking cessation in reducing the risk of both conditions.
Can Emphysema Turn into Cancer?
Emphysema does not turn into lung cancer. However, the chronic lung damage and inflammation associated with emphysema can create an environment that increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer. The presence of emphysema may indicate a higher risk for lung cancer, but they remain separate diseases.
Respiratory Health and Prevention
How Does Smoking Affect Emphysema and Lung Cancer?
Smoking is the leading cause of both emphysema and lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke cause direct damage to lung tissue, leading to chronic inflammation and destruction of the alveoli in emphysema. In lung cancer, smoking introduces carcinogens that can cause genetic mutations and uncontrolled cell growth. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of developing both conditions.
What Are the Risk Factors for Emphysema?
In addition to smoking, several factors can increase the risk of developing emphysema:
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke from others’ cigarettes.
- Air Pollution: Environmental pollutants can contribute to lung damage.
- Occupational Hazards: Inhalation of dust, chemicals, and fumes in the workplace.
- Genetics: Certain genetic factors, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, can increase the risk of developing emphysema.
- Age: The risk of emphysema increases with age due to the natural decline in lung function.
What Are the Risk Factors for Lung Cancer?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing lung cancer, including:
- Smoking: The leading cause of lung cancer, responsible for about 90% of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Inhalation of smoke from others can also increase risk.
- Radon Exposure: A radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and increase cancer risk.
- Asbestos Exposure: Occupational exposure to asbestos fibers.
- Family History: Genetics can play a role in lung cancer risk.
- Environmental Pollutants: Air pollution and exposure to certain chemicals.
Can Emphysema Be Prevented?
Preventing emphysema primarily involves reducing exposure to known risk factors. Key preventive measures include:
- Quitting Smoking: The most effective way to prevent emphysema.
- Avoiding Secondhand Smoke: Limiting exposure to smoke from others.
- Protecting Against Occupational Hazards: Using protective equipment and following safety guidelines in the workplace.
- Minimizing Exposure to Air Pollution: Staying indoors on high pollution days and using air purifiers.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Monitoring lung function and seeking early treatment for respiratory issues.
How is Emphysema Treated?
While there is no cure for emphysema, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics to manage symptoms and prevent infections.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen to help maintain adequate oxygen levels.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Exercise and education programs to improve lung function and overall health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, avoiding pollutants, and adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Surgery: In severe cases, procedures such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant may be considered.
What is the Prognosis for Emphysema?
The prognosis for individuals with emphysema varies depending on the severity of the disease, overall health, and lifestyle choices. While the disease is progressive and chronic, early diagnosis and proper management can help slow its progression and improve quality of life. Patients who quit smoking and adhere to their treatment plan often experience better outcomes.
What is the Difference Between Emphysema and Lung Cancer?
While emphysema and lung cancer are both serious lung diseases, they are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Here are the key differences:
- Nature of the Disease: Emphysema is a chronic lung disease characterized by the destruction of alveoli, while lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lungs.
- Causes: Emphysema is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, while lung cancer is most commonly linked to smoking but can also result from genetic factors, radon exposure, and other environmental pollutants.
- Symptoms: While both diseases share symptoms like shortness of breath and chronic cough, lung cancer often presents additional symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, coughing up blood, and tumor formation.
- Diagnosis: Emphysema is diagnosed through pulmonary function tests, imaging, and blood gas analysis, while lung cancer diagnosis involves imaging tests, biopsies, and molecular testing.
- Treatment: Emphysema treatment focuses on symptom management and improving lung function through medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes. Lung cancer treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Conclusion
Emphysema and lung cancer are distinct but related health conditions that share common risk factors, particularly smoking. Understanding the differences between these diseases, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining respiratory health. Quitting smoking, reducing exposure to pollutants, and seeking early medical intervention are key steps in managing and preventing these serious lung diseases.
FAQs
Q: Is emphysema a form of cancer?
A: No, emphysema is not a form of cancer. It is a chronic lung condition characterized by the destruction of the air sacs in the lungs.
Q: Can emphysema increase the risk of cancer?
A: Yes, individuals with emphysema, especially those who smoke, might have a slightly higher risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as lung cancer.
Q: What are the common symptoms of emphysema?
A: Common symptoms of emphysema include shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, chest tightness, and increased mucus production.
Q: How is cancer detected and diagnosed?
A: Cancer is often detected through screenings, diagnostic imaging, biopsies, and other medical tests, depending on the type and suspected location of the cancer.
Q: Can quitting smoking reduce the risk of emphysema and cancer?
A: Yes, quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of both emphysema and cancer. It’s never too late to quit and improve your health.