What Causes Throat Cancer: Throat cancer – Symptoms and causes
Causes of throat cancer at risk
It is well known that drinking alcohol and smoking tobacco are two of the main risk factors for throat cancer. This covers all smoked and smokeless tobacco products, such as cigars, pipes, cigarettes, chewing tobacco, snuff, and betel quid, and all sorts of alcoholic beverages, such as whiskey, beer, and wine.
Throat cancer, often a result of complex interactions between genetics and environmental factors, demands our attention. As we navigate through the labyrinth of causative agents, it becomes evident that awareness is our first line of defense against this formidable foe.
Understanding Throat Cancer: Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
Throat cancer, encompassing malignancies of the pharynx, larynx, vocal cords, and tonsils, is a serious condition with various causes and risk factors. While it predominantly affects individuals over 65 and is significantly more common in men, understanding its etiology and risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection.
Risk Factors for Throat Cancer
Tobacco Use and Throat Cancer Risk
One of the most significant risk factors for throat cancer is tobacco use. Whether through smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using smokeless tobacco products such as chewing tobacco and snuff, tobacco contains carcinogens that contribute to genetic mutations in throat cancer. The harmful substances in tobacco can cause severe damage to the DNA in throat cells, leading to throat cancer.
Alcohol Consumption and Throat Cancer
Excessive alcohol consumption also plays a major role in the development of throat cancer. The combination of alcohol and tobacco significantly increases the risk due to their synergistic effect on cellular DNA. Chronic exposure to alcohol can exacerbate the damage caused by tobacco, making moderation a key aspect of lifestyle factors leading to throat cancer.
Also, read about Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
HPV and Throat Cancer

The human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV types 16 and 18, is increasingly recognized as a cause of throat cancer. HPV and throat cancer have a strong link, with the virus contributing to the development of cancers in the oropharynx, including the tonsils and base of the tongue. Understanding and managing HPV exposure, including vaccination, is essential for reducing the risk of this particular form of cancer.
Environmental Triggers for Throat Cancer
Exposure to certain environmental triggers for throat cancer is another critical risk factor. Carcinogens found in asbestos, wood dust, paint fumes, and other industrial chemicals can increase the likelihood of developing throat cancer. Those working in high-risk industries should take preventive measures to reduce exposure to these harmful substances.
Diet and Throat Cancer Correlation
A poor diet, particularly one lacking in fruits and vegetables, has been associated with an increased risk of throat cancer. Diet and throat cancer correlation shows that a diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients can help fortify the body’s defenses against cancerous growths. Consuming a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables supports overall throat health and reduces cancer risk.
Genetic Predispositions for Throat Cancer
Genetic factors also play a role in the risk of throat cancer. Genetic predispositions for throat cancer include individuals with a family history of the disease or specific genetic mutations that increase susceptibility. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for those with a family history of throat cancer, helping to implement personalized preventive strategies.
Chronic Irritation and Throat Cancer
Chronic irritation from conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can contribute to the development of throat cancer. The constant acid exposure from GERD leads to inflammation and cellular changes in the throat lining, providing a conducive environment for cancer development. Effective management of GERD through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment is crucial for reducing associated cancer risks.
Viral Infections as Throat Cancer Causes
Besides HPV, other viral infections like the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) have been linked to throat cancer. Viral infections as throat cancer causes demonstrate how certain viruses can contribute to the malignancy by altering cellular DNA and immune responses.
Occupational Hazards Leading to Throat Cancer
Exposure to toxic substances in the workplace is a significant occupational hazard leading to throat cancer. Those in industries such as construction, metalworking, and textiles may encounter harmful chemicals that increase cancer risk. Implementing safety measures and using protective equipment can help mitigate these risks.
Throat Cancer and Family History
A family history of throat cancer can be a strong indicator of increased risk. Throat cancer and family history suggest that genetic factors combined with environmental exposures can heighten the likelihood of developing the disease. Individuals with a family history should consider regular screenings and genetic counseling to manage their risk.
Autoimmune Disorders and Throat Cancer
Certain autoimmune disorders may also be linked to throat cancer. Conditions that cause chronic inflammation or immune dysregulation can increase cancer risk. Monitoring and managing these disorders are important for reducing overall cancer risk.
Impact of Gastroesophageal Reflux on Throat Cancer
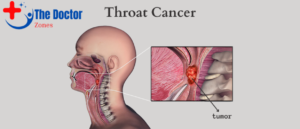
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) not only contributes to chronic throat irritation but also increases the risk of throat cancer. The persistent reflux of stomach acids can lead to cellular damage and mutations in the throat lining, emphasizing the importance of addressing GERD to prevent cancer development.
Prevention and Management
While complete prevention of throat cancer may not be feasible, several strategies can significantly reduce the risk:
- Avoid tobacco use and limit alcohol consumption to mitigate the risks associated with these behaviors.
- Vaccinate against HPV to protect against the types of the virus linked to throat cancer.
- Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables to support throat health and reduce cancer risk.
- Use protective gear in occupational settings to minimize exposure to harmful chemicals and carcinogens.
- Manage chronic conditions such as GERD and autoimmune disorders to reduce their impact on throat health.
Conclusion
In summary, throat cancer arises from a complex interplay of risk factors, including lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and genetic predispositions. By understanding and addressing these factors, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their risk and enhancing overall throat health. Regular screenings and adopting a healthy lifestyle are key components in the fight against throat cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can throat cancer be completely prevented?
While complete prevention is not possible, avoiding risk factors like tobacco and excessive alcohol, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing chronic conditions can significantly reduce the risk.
Q: How often should individuals at high risk be screened for throat cancer?
Individuals with a family history or significant risk factors should undergo regular screenings, ideally annually, to detect any early signs of throat cancer.
Q: Are there new treatments for throat cancer?
Yes, ongoing research is leading to advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies, providing new options for effective treatment.
Q: How can HPV-related throat cancer be prevented?
HPV vaccination and practicing safe sexual behaviors can reduce the risk of HPV-related throat cancer.
Q: What support is available for throat cancer patients?
Supportive therapies, including counseling, support groups, and complementary therapies like acupuncture, can help manage the emotional and physical challenges of throat cancer treatment.